The IPO grey market has emerged as a significant component of India’s investment landscape, providing early insights into market sentiment before official stock listings. As India leads global IPO activity with a robust pipeline of offerings, understanding the IPO grey market dynamics becomes crucial for investors seeking to capitalize on pre-listing opportunities. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of IPO grey market trading, its mechanisms, benefits, risks, and current market trends.
What is IPO Grey Market?
The IPO grey market refers to an unofficial, unregulated marketplace where shares of upcoming Initial Public Offerings are traded before their official listing on stock exchanges like NSE and BSE. This informal market operates outside SEBI’s regulatory framework, functioning on trust-based agreements between participants. The IPO grey market becomes active immediately after a company announces its IPO and continues until the shares are officially listed for regular trading.
Unlike official stock exchanges, the IPO grey market operates through informal networks of dealers and brokers who facilitate transactions based on supply and demand dynamics. These trades are settled manually, typically in cash, without the sophisticated clearing and settlement mechanisms available on formal exchanges.
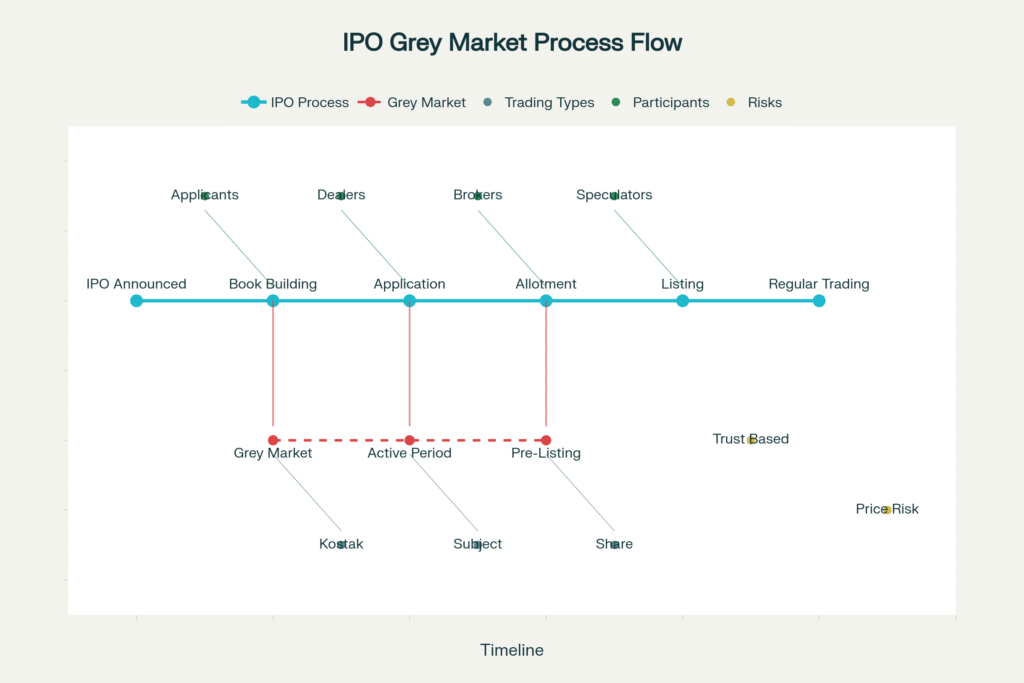
IPO grey market process flow showing the complete journey from announcement to listing with key trading opportunities and risks
Understanding Grey Market Premium (GMP)
Grey Market Premium (GMP) is the cornerstone of IPO grey market activity, representing the additional amount investors are willing to pay above the IPO issue price. For example, if an IPO has an issue price of ₹100 and trades at ₹150 in the IPO grey market, the GMP would be ₹50, indicating a 50% premium.
Current market analysis reveals that the average GMP across major IPOs stands at approximately ₹62, with an average percentage premium of 20.1%. Companies like Jinkushal Industries command premium rates as high as 43%, while others maintain more conservative premiums around 11-15%.
ipo_grey_market_analysis.csv
Generated File
The GMP calculation follows a simple formula:
GMP = Grey Market Price – Issue Price
GMP Percentage = (GMP ÷ Issue Price) × 100
This metric serves as a market sentiment indicator, helping investors gauge expected listing performance and overall demand for the IPO.
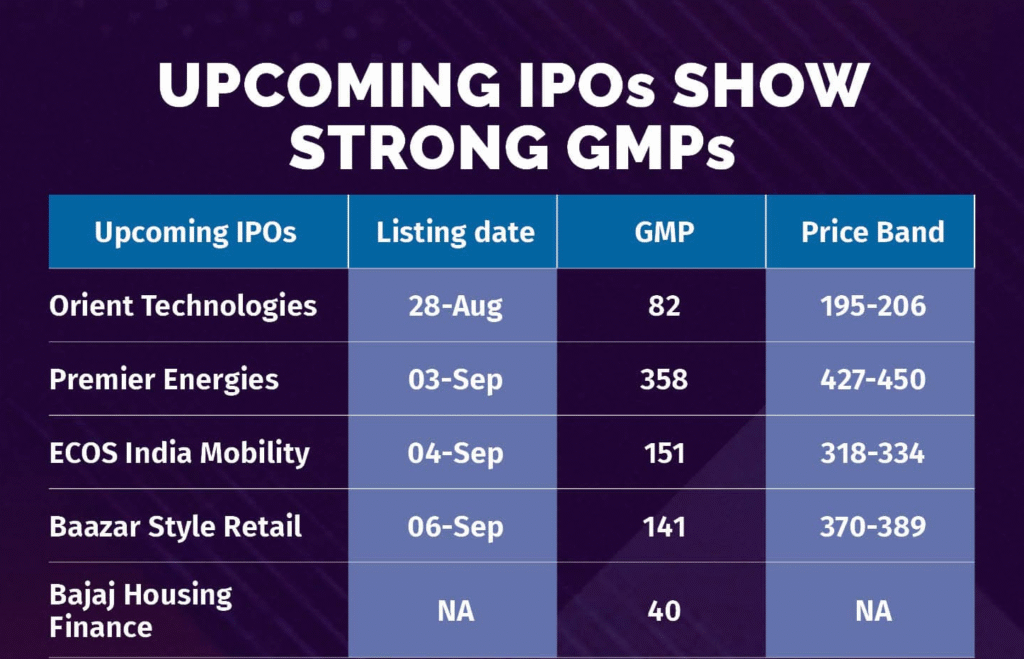
Table showing grey market premiums (GMP) for upcoming IPOs in India with listing dates and price bands
Types of IPO Grey Market Trading
The IPO grey market operates through two primary trading mechanisms, each catering to different risk appetites and investment strategies.
Kostak Trading
Kostak trading involves selling IPO applications regardless of allotment status. In this arrangement, the seller receives a predetermined amount from the buyer, irrespective of whether shares are allocated or the stock’s listing performance. For instance, if the Kostak rate is ₹300, the seller receives this amount even if no shares are allotted or if the stock lists below the issue price.
Subject to Trading
“Subject to” trading offers higher premiums but carries greater risk. Here, the buyer pays a premium only if shares are actually allotted to the seller. If no allotment occurs, the transaction is canceled. This mechanism allows for potentially higher profits but requires actual share allocation for completion.
Recent market data shows SME IPOs averaging 26.25% GMP compared to 18.51% for mainboard offerings, reflecting the higher volatility and speculative interest in smaller company offerings.
How IPO Grey Market Works
The IPO grey market operates through a network of intermediaries who connect buyers and sellers. The process typically unfolds as follows:
Pre-IPO Phase: Once a company announces its IPO dates, grey market dealers begin quoting preliminary rates based on company fundamentals and market conditions.
Active Trading Period: During the book-building and application period, intensive trading occurs as dealers adjust prices based on subscription levels and institutional interest.
Post-Allotment Activity: After allotment results are announced, final settlements occur as shares are transferred and payments completed.
The entire IPO grey market ecosystem relies on personal relationships and trust networks, with most transactions conducted through phone calls and informal agreements.
Ceremonial bell ringing at NSE marking the listing event related to Transform Rural India (TRI)
Benefits of IPO Grey Market
Early Price Discovery
The IPO grey market provides valuable price discovery mechanisms, offering insights into market expectations before official listing. This early indication helps investors make informed decisions about participation in the IPO or immediate exit strategies.
Liquidity Opportunities
Investors can exit positions before official listing through grey market transactions, providing liquidity that would otherwise be unavailable during the pre-listing period. This flexibility allows for profit-taking or loss mitigation based on changing market conditions.
Market Sentiment Gauge
GMP levels serve as effective barometers of market sentiment, reflecting institutional and retail investor confidence in specific offerings. High GMP rates often indicate strong demand and positive listing expectations.
Risks and Challenges
Regulatory Absence
The most significant risk in IPO grey market trading stems from the complete absence of regulatory oversight. Unlike official exchanges, there are no SEBI protections, settlement guarantees, or dispute resolution mechanisms.
Counterparty Risk
All grey market transactions depend entirely on trust between participants. If either party defaults, investors have no legal recourse or regulatory protection, potentially resulting in complete loss of invested capital.
Price Manipulation
Due to its informal nature, the IPO grey market remains susceptible to price manipulation by unscrupulous dealers who may inflate or deflate GMP rates to create artificial market sentiment.
Settlement Risks
Manual settlement processes increase the probability of disputes, delayed payments, or non-delivery of shares, particularly during volatile market conditions.
Current Market Trends and Analysis
Recent IPO grey market analysis reveals interesting sector-wise performance patterns. Industrial companies lead with an average GMP percentage of 42.97%, followed by cables (28.94%) and textile sectors (23.56%). Technology companies maintain moderate premiums around 16.56%, while traditional energy sectors show more conservative 15.03% rates.
The market demonstrates clear bifurcation between risk categories, with 40% of current IPOs falling into moderate risk brackets (15-25% GMP), another 40% in conservative ranges (below 15%), and 20% in high-risk/high-reward categories (above 25%).
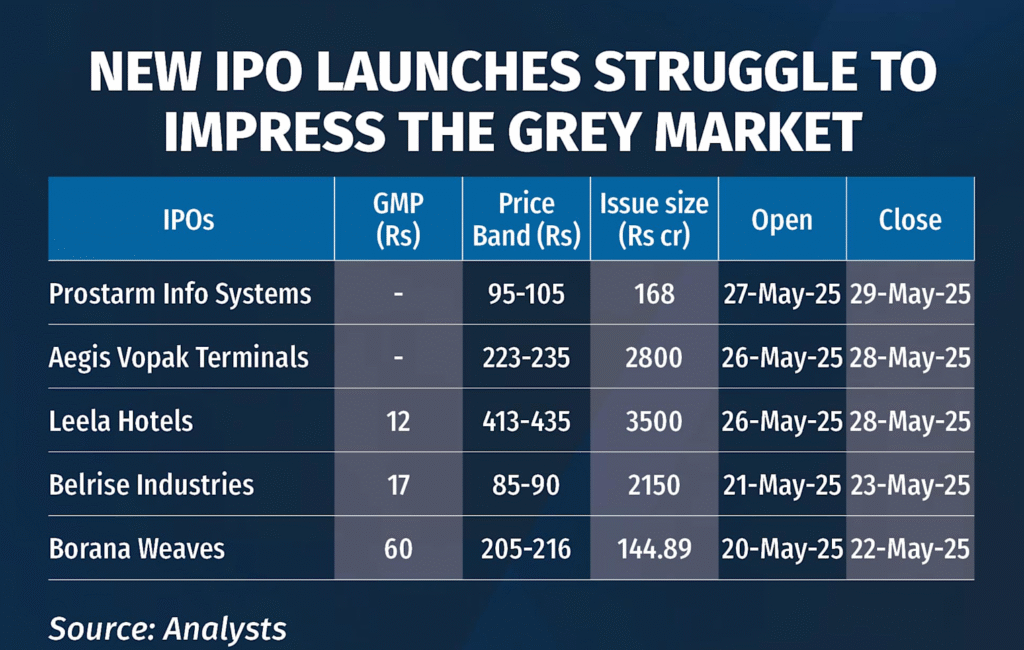
Table showing new IPO launches with their grey market premium (GMP), price band, issue size, and listing dates indicating struggle to impress the grey market
SEBI’s Regulatory Response
Recognizing the growing influence of IPO grey market activity, SEBI is developing a “when-listed” platform to provide regulated pre-listing trading opportunities. This initiative aims to bring transparency and regulatory oversight to currently informal grey market activities while maintaining legitimate price discovery benefits.
The proposed framework would feature licensed intermediaries, standardized documentation, and established settlement practices, potentially reducing risks associated with current grey market operations. Former SEBI chairperson Madhabi Puri Buch indicated that this platform would allow investors to trade shares immediately after allotment, even before official listing.
Investment Strategies for Grey Market Participants
Fundamental Analysis Priority
Successful IPO grey market participation requires thorough fundamental analysis of underlying companies rather than relying solely on GMP trends. Investors should evaluate business models, financial health, and growth prospects before making grey market commitments.
Risk Management
Given the unregulated nature of grey market trading, investors should limit exposure to amounts they can afford to lose entirely. Diversification across multiple IPOs and avoiding concentration in single offerings helps mitigate counterparty and market risks.
Timing Considerations
Grey market prices fluctuate significantly based on broader market conditions, subscription levels, and institutional interest. Monitoring these factors helps optimize entry and exit timing for grey market positions.
Group photo at the NSE and KFin Technologies IPO bell ringing ceremony event
Recent Performance Analysis
Analysis of recent IPO grey market activity shows mixed results compared to actual listing performance. Research indicates that over 60% of IPOs debut below their GMPs, with approximately 40% falling short of Kostak rates. This data underscores the importance of treating GMP as an indicative rather than predictive tool.
However, certain sectors and company types consistently outperform grey market expectations. Technology companies and those with strong institutional backing often exceed GMP predictions, while traditional manufacturing and commodity-based businesses may underperform expectations.
Best Practices for Grey Market Trading
Verification and Due Diligence
Always verify grey market quotes from multiple dealers to ensure accuracy and avoid manipulation. Cross-referencing rates across different platforms helps identify realistic market levels.
Documentation
Despite the informal nature, maintain records of all grey market transactions, including dealer contact information, agreed rates, and transaction dates. This documentation proves valuable for tax purposes and dispute resolution.
Trusted Networks
Work exclusively with established dealers who have proven track records and references from other participants. The IPO grey market operates primarily on reputation and trust relationships.
Future Outlook
The IPO grey market is poised for significant evolution as regulatory frameworks develop and market sophistication increases. SEBI’s planned “when-listed” platform represents a major step toward formalizing pre-listing trading activities while maintaining beneficial price discovery mechanisms.
Technology integration may also transform grey market operations, potentially introducing digital platforms that enhance transparency while maintaining the flexibility that makes grey market trading attractive to participants.
As India continues leading global IPO activity with substantial retail participation, the IPO grey market will likely remain an integral component of the broader capital markets ecosystem, albeit with increased regulation and oversight.
Conclusion
The IPO grey market serves as a crucial barometer of investor sentiment and provides valuable price discovery mechanisms in India’s dynamic capital markets. While offering opportunities for early access and profit realization, grey market trading carries inherent risks due to its unregulated nature and trust-based operations.
Successful participation in the IPO grey market requires careful risk assessment, thorough fundamental analysis, and working with trusted counterparties. As regulatory frameworks evolve and market infrastructure develops, the IPO grey market will likely become more transparent and accessible while maintaining its role as an important component of India’s IPO ecosystem.
Investors considering grey market participation should view it as one tool among many in their investment strategy, always prioritizing company fundamentals over short-term grey market premiums. With proper understanding and risk management, the IPO grey market can provide valuable insights and opportunities for informed investors navigating India’s vibrant IPO landscape.








Leave a Reply